Sunspot date vs CO2: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Roger Coppock Facebook 1/29/21 Answers in Climate Science 2f3tSp tenomnshrorusiedS · The Sunspot Scapegoat Fossil fools, in their never ending search for something ot...") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Roger Coppock Facebook 1/29/21 Answers in Climate Science | Roger Coppock Facebook 1/29/21 Answers in Climate Science | ||
[[File:Temp vs Sunspots.jpg|left|thumb|GISS 4 Temperature Vs Sunspots]] | |||
[[File:Temp vs CO2.jpg|left|thumb|GISS V4 Temperature vs Mauna Loa CO2]] | |||
The Sunspot Scapegoat | The Sunspot Scapegoat | ||
Fossil fools, in their never ending search for something other than their master's oil, coal, and gas products that is the major cause of global warming, have at times blamed sunspots. They produce cherry picked proxy series and collections of anecdotes to try to support this. Often the bafflegab mentions the "Maunder minimum" and the "little ice age." These events occurred in the late 17th century, long before modern instruments could accurately record them. However, today's directly observed data tell a different story. Actual sunspot count data barely show any correlation with the global land and sea surface temperature from 1958 to 2020. | Fossil fools, in their never ending search for something other than their master's oil, coal, and gas products that is the major cause of global warming, have at times blamed sunspots. They produce cherry picked proxy series and collections of anecdotes to try to support this. Often the bafflegab mentions the "Maunder minimum" and the "little ice age." These events occurred in the late 17th century, long before modern instruments could accurately record them. However, today's directly observed data tell a different story. Actual sunspot count data barely show any correlation with the global land and sea surface temperature from 1958 to 2020. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:22, 29 January 2021
Roger Coppock Facebook 1/29/21 Answers in Climate Science

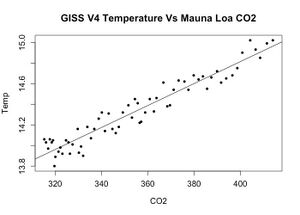
The Sunspot Scapegoat Fossil fools, in their never ending search for something other than their master's oil, coal, and gas products that is the major cause of global warming, have at times blamed sunspots. They produce cherry picked proxy series and collections of anecdotes to try to support this. Often the bafflegab mentions the "Maunder minimum" and the "little ice age." These events occurred in the late 17th century, long before modern instruments could accurately record them. However, today's directly observed data tell a different story. Actual sunspot count data barely show any correlation with the global land and sea surface temperature from 1958 to 2020. The scatter graph of global mean near-surface temperature vs. sunspots shows little relationship. What tiny effect there is looks like an inverse one; sunspots cause cooling. <TempV4VsSunspots.jpg> Small Sample R-squared=0.05 p-value=0.05 The numbers above say there is little connection, and even that is 5% likely due to chance. (Please, see the note at the bottom.) Meanwhile, the temperature and CO2 are at the other extreme. They are very tightly bound together. <CO2TempV4.jpg> Small Sample R-squared=0.92 p-value=~1.4e-35 Here the numbers tell us that there is a very strong connection, and that it is not due to chance. Sources of Data Yearly mean temperature data are NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies Version 4 at: https://data.giss.nasa.gov/.../tabledata_v4/GLB.Ts+dSST.txt Yearly mean atmospheric CO2 concentration are from the NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory: ftp://aftp.cmdl.noaa.gov/products/trends/co2/co2_mm_mlo.txt This record begins in 1958, when Charles Keeling started measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations atop mount Mauna Loa. The data are known as the "Keeling Curve." Yearly mean total sunspot number data are from the World Data Center for the Sunspot Index Royal Observatory of Belgium: https://www.quandl.com/.../SUNSPOTS_A-Total-Sunspot... where the comma separated variable file, "SIDC-SUNSPOTS_A.csv" was downloaded. THE DATA Year Temp CO2 Sunspots 1958 14.06 315.2320 261.7 1959 14.03 315.9808 225.1 1960 13.97 316.9100 159.0 1961 14.06 317.6442 76.4 1962 14.03 318.4542 53.4 1963 14.05 318.9925 39.9 1964 13.80 319.6167 15.0 1965 13.89 320.0358 22.0 1966 13.94 321.3692 66.8 1967 13.98 322.1808 132.9 1968 13.92 323.0500 150.0 1969 14.05 324.6233 149.4 1970 14.03 325.6817 148.0 1971 13.92 326.3192 94.4 1972 14.01 327.4567 97.6 1973 14.16 329.6775 54.1 1974 13.93 330.1842 49.2 1975 13.99 331.1192 22.5 1976 13.90 332.0400 18.4 1977 14.18 333.8317 39.3 1978 14.07 335.4033 131.0 1979 14.16 336.8408 220.1 1980 14.26 338.7508 218.9 1981 14.32 340.1050 198.9 1982 14.14 341.4475 162.4 1983 14.31 343.0542 91.0 1984 14.16 344.6600 60.5 1985 14.12 346.1158 20.6 1986 14.18 347.4325 14.8 1987 14.32 349.1817 33.9 1988 14.39 351.5692 123.0 1989 14.27 353.1225 211.1 1990 14.45 354.3933 191.8 1991 14.41 355.6117 203.3 1992 14.22 356.4450 133.0 1993 14.23 357.1000 76.1 1994 14.32 358.8325 44.9 1995 14.45 360.8200 25.1 1996 14.33 362.6075 11.6 1997 14.46 363.7292 28.9 1998 14.61 366.6992 88.3 1999 14.38 368.3817 136.3 2000 14.39 369.5500 173.9 2001 14.54 371.1442 170.4 2002 14.63 373.2792 163.6 2003 14.62 375.8017 99.3 2004 14.54 377.5225 65.3 2005 14.68 379.7958 45.8 2006 14.64 381.8992 24.7 2007 14.67 383.7908 12.6 2008 14.55 385.5950 4.2 2009 14.66 387.4300 4.8 2010 14.72 389.8992 24.9 2011 14.61 391.6517 80.8 2012 14.65 393.8550 84.5 2013 14.68 396.5200 94.0 2014 14.75 398.6425 113.3 2015 14.90 400.8258 69.8 2016 15.02 404.2225 39.8 2017 14.93 406.5550 21.7 2018 14.85 408.5200 7.0 2019 14.99 411.4342 3.6 2020 15.02 414.0067 8.7 -.-. --.- -.. . Roger Coppock (Those who are new to statistical correlation and "R squared" will find a tutorial on the subject here: http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Correlation.html http://mathworld.wolfram.com/CorrelationCoefficient.html Item 20 in the above shows R squared for several graphed relationships.) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Here's something extra on my post, "The Sunspot Scapegoat," for those who know science. It's the mathematics Milankovitch used to find his cycles, multiple linear regression. (For information on Milankovitch Cycles, see: https://climate.nasa.gov/.../milankovitch-orbital-cycles.../ ) The hypothesis is that global yearly mean temperature is the sum of CO2 and Sunspots. Note that in this model CO2 carries all the weight, and yearly mean sunspot counts hardly contribute anything by comparison. This is exactly what the individual CO2 and sunspot correlations and regressions found in my first post. summary(lm(Temp ~ CO2 + Sunspots)) Call: lm(formula = Temp ~ CO2 + Sunspots) Residuals: Min 1Q Median 3Q Max -0.15396 -0.07504 -0.00713 0.07191 0.16515 Coefficients: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) (Intercept) 1.04e+01 1.53e-01 68.12 <2e-16 *** CO2 1.08e-02 4.16e-04 26.06 <2e-16 *** Sunspots 4.12e-04 1.71e-04 2.41 0.019 * --- Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1 Residual standard error: 0.0878 on 59 degrees of freedom Multiple R-squared: 0.924, Adjusted R-squared: 0.921 F-statistic: 359 on 2 and 59 DF, p-value: <2e-16
